What is whole plant analysis?

Whole plant analysis is like a plant tissue test. Instead of measuring the nutrient content in just the leaf,we measure the whole plant.
The difference is that we can look at not only the nutrient content of the plant to look for deficiencies, but also calculate the nutrient removal and crop potential.
What are the uses and timing for whole plant analysis?
From Planting to Tassel:
We can identify nutrient limitations, and benchmark our nutrient removal. The more N,P,K, etc you can get out of the ground early in the season, the more you have the potential to remove later. Last year we observed a 100 lb difference in N removed at the V10 growth stage. The fields with more N out of the ground early ended up removing 200-300 lbs of N at the end of the season. Fields with less out of the ground earlier removed significantly less at the end of the year.
Just Before Harvest:
By measuring nitrogen removal at the end of the season we can gain insight on how effective a nitrogen program was. Did you remove all the nitrogen you applied? Did your soil mineralize nitrogen over and above what you applied? In the chart you can see that the nitrogen removed from the ground (blue) varied from 400 to 100 lbs in 2016.
For the 2017 growing season consider whole plant analysis to better understand your nutrient limitations and refine your nitrogen program.
Plant Tissue vs Whole Plant
| Plant Tissue | Whole Plant | |
| Nutrient Limitations | ✓ | ✓ |
| Nutrient Removal | ✓ | |
| Crop Potential | ✓ |
Whole Plant Report Report Features
Report Features
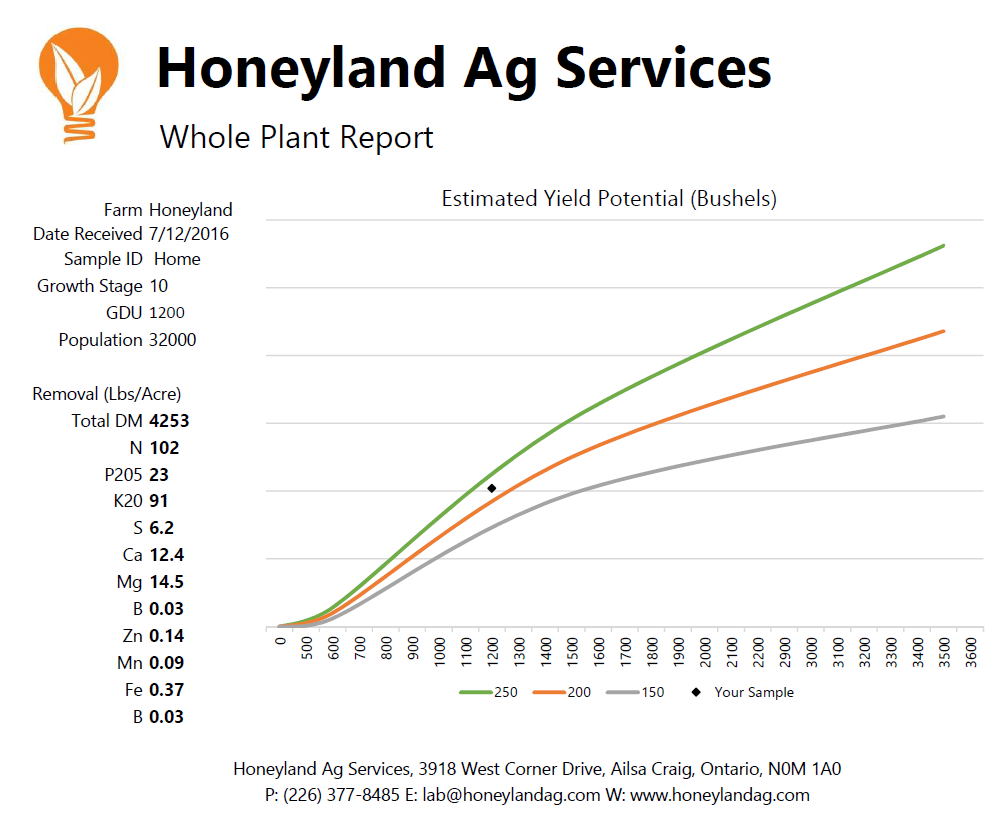
- Estimated Yield Potential – Establish the potential of the crop and estimate the nitrogen required to finish the crop without limiting yield.
- Crop Removal – Calculation of the removal of nutrients from the ground.
- Sufficiency Ranges – Like a plant tissue analysis, determine which nutrients are limiting.
- Separate Removal for Plant and Ear (after tasseling)
Tips for Whole Plant Sampling
- It is important to sample field variation (soil types, light/dark/high/low spots) separately.
- Sample average plants (look at height of the plant, stalk thickness, leaf burn and cob size Take a minimum of 4 stalks.
- Cut stalks off one inch from the ground.
Packages
- Standard ($30 Pre Tassel, $40 Post Tassel): Removal of N, P, K, S, Mg, Ca, Na, Zn, Fe, Mn, Cu, B
- Ear Option: ($10) Separate analysis of ear for N, P, K, S, Mg, Ca, Na, Zn, Fe, Mn, Cu, B
Whole Plant Tracker
- Track your nutrients remove from the ground through the growing season.
- Tired of flipping between pages? Compare good/poor areas of fields on the same report.
- All data is tracked by GDU to provide a fair comparison between fields planted at different times.
- Reports for both plant composition and lbs of nutrient removal.